The physical branch has been the primary sales channel for traditional banks, even as the broader business increasingly becomes digitalized. However, decreased foot traffic, digitally savvy consumers, competitive threats, artificial intelligence (AI), and technology transformation all challenge the status quo, demanding the digitalization of marketing and sales. Given the complexity of the value chain, this requires transformational change. This Viewpoint sets out an eight-stage approach to delivering digital sales success for banks.
FINANCIAL SERVICES MARKETING MUST GO DIGITAL
Retail banks have invested heavily to digitalize their operations, especially transactional channels like mobile and online banking. At the same time, the function of the physical branch has shifted from simple sales and service to providing personalized, face-to-face advice that drives sophisticated, high-value product sales.
But the world is changing, and today’s banks are experiencing an evolution:
-
Decreased foot traffic.
-
Digitally savvy consumers, in part due to the pandemic, accelerated the shift to digital faster than banks expected and a digital disconnect between offerings and expectations emerged.
-
Greater competition from nimbler, digital fintech rivals, accelerated by the rise of open banking and a threat of disintermediation.
-
The ever-growing need to invest in digital to find and create leads (according to Nielsen, the global banking media spend averages 3.8%, although this varies widely; brands in Asia-Pacific invest 4.6% of revenues while those in North America spend 4.1%, yet enjoy 15% higher ROI).
-
A requirement to better understand their audiences to drive higher returns on digital investment (successful brands can achieve an average ROI of $2 to $3 per $1 spent through effective targeting of messages and channels, as reported by Nielsen).
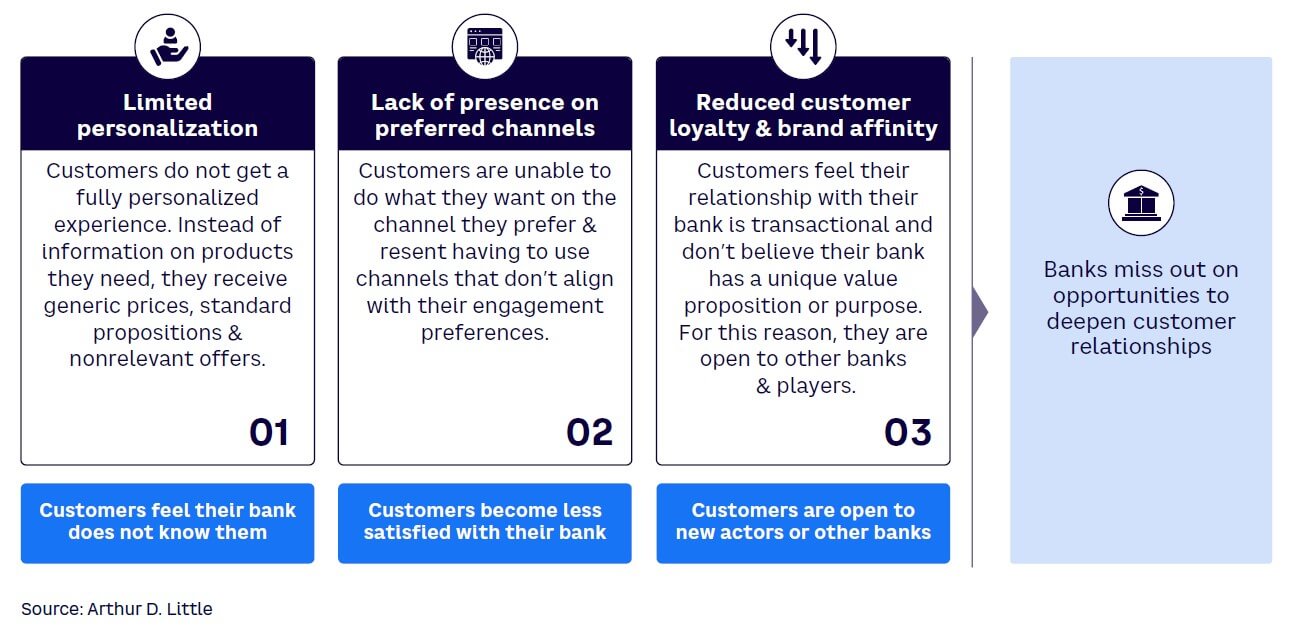
Current digital sales channels are typified by high customer acquisition costs and are driven primarily by online advertising spend. They will be severely impacted by forthcoming bans on cookies, which will make it harder to recognize and target potential buyers, preventing integrated, personalized marketing to prospects.[1] Brands are already seeing many customers opting out of marketing channels. All of this results in limited personalization, a lack of bank presence on preferred consumer channels, and reduced customer loyalty (see Figure 1).
OVERCOMING DIGITAL MARKETING CHALLENGES
In this new world of banking, banks need to focus on AI as a way to modernize their digital marketing strategy and operations or face lost customers and revenues. This shift has huge implications for their end-to-end operating model and the resources and skills required in their sales and marketing organizations.
Banks should prioritize four strategies to address their challenges:
-
Humanize digital interactions. Understand key customer pain points and provide empathetic support to engage with customers.
-
Reinvigorate brand purpose. Refine brand purpose to ensure it is clear to consumers and engages the community.
-
Empower and trust technology. Invest in data to power digital marketing and trust AI and machine learning (ML) algorithms to deliver on customer needs in real time and at scale.
-
Reimagine branches. Remodel and restructure branch networks to provide tailored advice that builds customer loyalty.
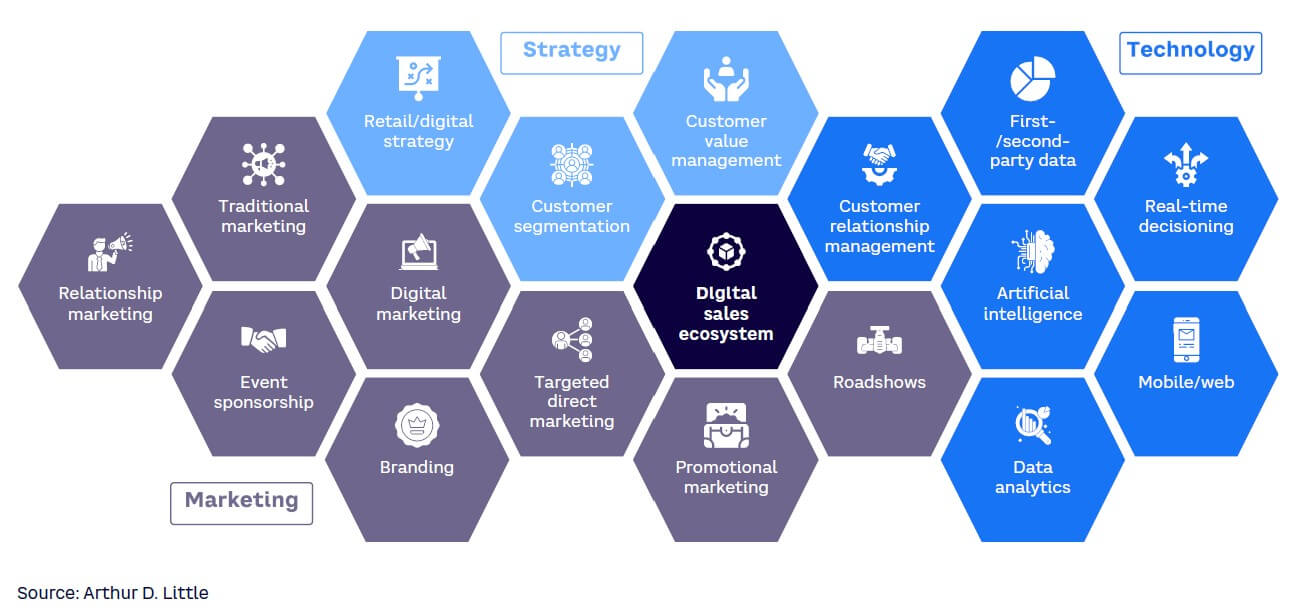
This shift is not just about marketing. It requires a combination of strategy and technology (particularly AI) to establish a comprehensive digital sales ecosystem (see Figure 2).
AN END-TO-END APPROACH
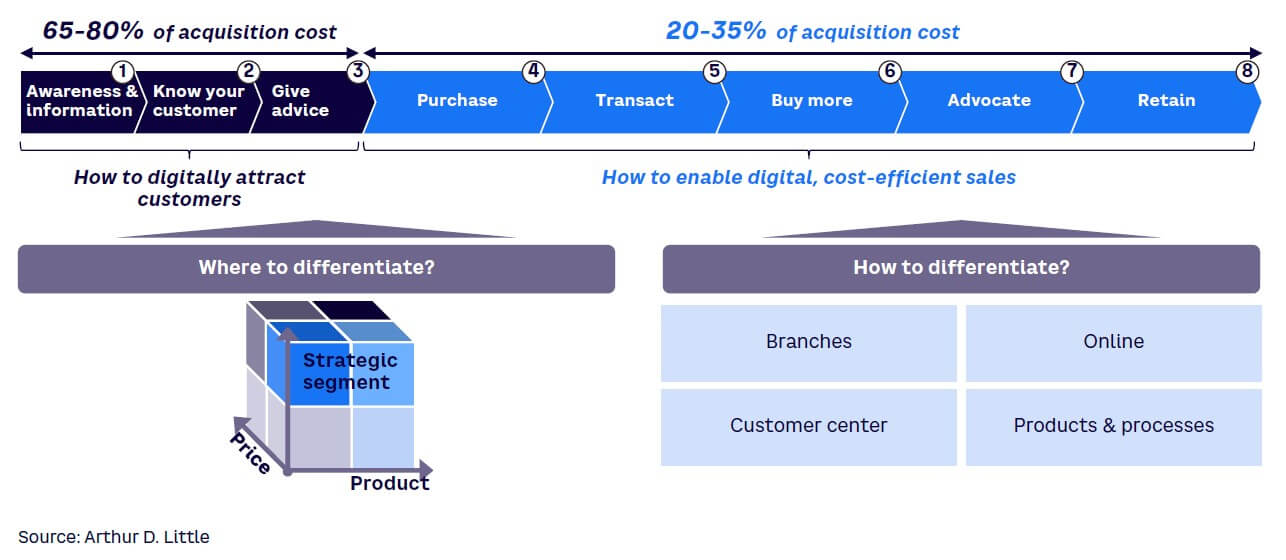
Banks must redesign their digital customer acquisition and experience strategy by identifying where and how to differentiate. This will deliver competitive advantage in both increased attraction and cost-effective sales execution. The modern customer journey is complex, spanning multiple steps and touchpoints. To plan and act effectively, banks must focus on a multi-stage approach that covers the entire digital customer journey (see Figure 3). Below are detailed descriptions of each stop along the way.
1. Begin with awareness & information
Regardless of how customers enter the sales funnel, their journey invariably involves research on digital channels. Given the range of channels and assets (spanning earned, owned, and paid approaches), banks must fully understand and optimize their digital client acquisition strategies. This starts with a clear search engine optimization (SEO) strategy that drives natural traffic to their sites and carefully tracks which assets and tactics deliver the best results.
A detailed, data-driven, full-funnel marketing strategy drives significant value. By shifting greater media allocation to areas with higher returns, employing test-and-learn optimization and automation for demand-generation campaigns, enriching company data, and implementing microtargeting, marketers can achieve a 15% to 20% increase in marketing ROI. It is vital that the awareness stage motivates potential clients to the point where they move forward on the customer journey.
2. Know your customer
Complying with know your customer (KYC) regulations is time-consuming and burdensome for customers and resource-intensive for banks. Digitalizing KYC benefits everyone, making it smoother, faster, and more efficient. This positively impacts the customer journey and decreases risks for banks.
To achieve this, banks must focus on the improvements that AI and blockchain technologies can deliver. Deploying AI allows banks to:
-
Better understand customer risk profiles based on access to larger data sources.
-
Apply biometric methods to confirm customer identity.
-
Reduce manual administration and potential errors through automation.
-
Lower risk through real-time transaction monitoring.
By taking advantage of blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT), banks remove the need to ask customers for KYC information. Instead, they access KYC documents within a distributed ledger, confident that they are accurate, up to date, immutable, and secure. This speeds up the process, streamlining KYC work, depending on the scale of automated reviews and share of customers subject to those processes, all while improving the customer experience. A recent market study reported by Temenos found that applying blockchain solutions through the customer onboarding process can create up to US $1 billion of savings in operating costs for retail banks globally and reduce regulatory fines by $2 billion to $3 billion.
3. Give advice
The consumer population is fragmented: some are hyper-informed, but the majority need advice on products and services. Regardless of their knowledge status, everyone expects solutions to be personalized to their needs. Banks should focus on delivering tailored advice based on an understanding of individual goals, providing relevant products that meet personalized objectives rather than trying to create new needs. This approach requires listening to customers and using enriched data and AI analysis to pinpoint where they are in their life and their specific circumstances (e.g., products already purchased).
Studies show companies that excel at personalization generate 40% more revenue from those activities than average players. Across US industries, shifting to top-quartile performance in personalization can generate more than $1 trillion in additional value, according to Coniq, a specialized customer solutions boutique. By recognizing a customer’s short-, medium- and long-term goals and matching products to these needs, banks can deliver greater value, generating both immediate sales and building trust for the future.
Leading US and European banks are already applying a need-based approach to providing advice. This includes building a deep understanding of a customer’s life stage, priorities, and motivations to provide personalized advice that drives new product sales and increases longer-term loyalty.
4. Streamline purchases
Less complex financial products are increasingly being purchased online, and as their sophistication increases, consumers will want to buy more complex products digitally as well. Making this process fast and seamless is a challenge, particularly when purchases require approval based on credit/KYC checks. To simplify this process, banks should introduce automatic approval, using a combination of internal data, ML, and external information from standards-based integration with third parties to provide accurate estimates of a customer’s payment capabilities.
A TD Bank project found that the implementation of an AI-powered loan origination system resulted in 30%-40% reduction in the time required for loan approvals and a 75% decrease in manual underwriting costs. The goal was to match the ubiquity and speed of buy-now-pay-later services like Klarna, which have changed the sales paradigm by embedding themselves within the e-commerce buying process. This approach also decreases the chance the bank will disappoint a customer by offering lending products that the customer may not be eligible for regarding credit approval.
A second way to simplify the purchase process is to preapprove multiple products. This removes the need to repeat the approval process, saving customers time, increasing efficiency, and boosting upselling. Maybank, Southeast Asia’s fourth largest bank, adopted this approach with One Solution, a bundle designed to consolidate the banking relationship. Customers apply once for all products in the bundle and provide all necessary information. They can then activate and access products as needed, using the channel of their choice. After initial nine months, One Solution customers have around twice the product holdings of average branch-served customers.
5. Optimize transactions
Customers are reducing their use of branches for transactions and services in favor of digital channels. This means all products need to be digitalized by default, with a focus on offering transactions via mobile and applications to increase convenience. Research by Google found that banks are achieving 20% revenue increases and up to 30% cost savings after their first phase of digital transformation.
Digitalizing the transaction process opens up opportunities to add value by moving beyond core banking requirements into wider personal financial management. It is now common for banks to offer add-on financial services in areas such as household expenditure management or money/fund management, often using third-party tools. These services create an ecosystem that covers more than just finance and lets banks sell complementary partner products.
For example, Australia’s Commonwealth Bank launched a mobile property app, demonstrating that it’s possible to digitalize the notoriously complex mortgage process. The app makes it easy to research homes and provides additional information when visiting properties via augmented reality. Covering most residential properties in Australia, it includes automated home valuation using market statistics and an integrated home repayment calculator.
6. Buy more
Banks need to focus on maximizing additional sales to customers through well-targeted, personalized product offers. The key is to leverage data to create relevant, compelling, automated cross-sell and up-sell opportunities by understanding demographics, context, behavior, and preferences. Using both customer life events and transaction history lets banks successfully create these propositions and deliver them at the right time to anticipate customer needs.
AI and ML are key to providing this at scale. For example, ADL worked on a product-recommendation engine for an SME/commercial bank. The project used two years of data to identify propensity to buy across 75 types of opportunities. When levels reached set thresholds, appropriate products were offered. This led to more than 10,000 opportunities to sell new products and 30,000 opportunities for additional products.
7. Advocate
Customers increasingly listen to and provide feedback on digital platforms, which is extremely valuable in driving improvements in overall satisfaction and individual products and interactions. It can also be used to drive business transformation and focus banking staff on the importance of the digital customer journey. By linking net promoter score (NPS) tracking results to staff remuneration, the focus shifts from how many products an individual or team has sold to overall customer satisfaction.
This increases company-wide service levels and turns satisfied customers into loyal brand advocates that champion the bank to their friends and social groups online and in the physical world. Loyal relationships translate into cost savings. According to Harvard Business Review, in financial services, a 5% increase in customer retention produces a 25% increase or more in profit. Current customers tend to buy more from a company over time, and higher product penetration both increases customer stickiness and reduces operating costs. Additionally, advertising to an existing customer base is significantly less expensive than acquiring new clients.
8. Retain
Too often, the first time a bank sees customer churn is when a bank account is closed or a product is switched. This is particularly true in the digital world, where there is little or no personal contact with bank staff. Using predictive analytics and AI to generate better understanding of client behaviors is key to driving specific, fast-retention actions.
Banks should model the churn propensity of specific customer profiles, then identify and design prevention actions based on customer value. These should be personalized as much as possible (especially for high-value customers) and should trigger when specific conditions around behavior are met. These could be internal, such as a customer coming to the end of a product deal, or external, either in reaction to competitor activity or macroeconomic factors like rising energy prices.
All retention-management activities should be monitored to track positive and negative impacts, with clear KPIs and the use of operational, customer, and financial scorecards. For example, it is possible to apply retention offers like discounts too broadly, pushing up costs. To minimize this risk, banks should remain in close contact with customers and understand their satisfaction levels through NPS to judge whether discounts are necessary (in some cases, the customer will remain without incentives).
CREATING AN AI-ENHANCED BANK
To meet the complex, increasingly digital needs of customers, banks should incorporate AI in key areas alongside digital marketing channels (see Figure 4). This will help them better understand their clients so they can meet their needs and sustain their competitiveness.
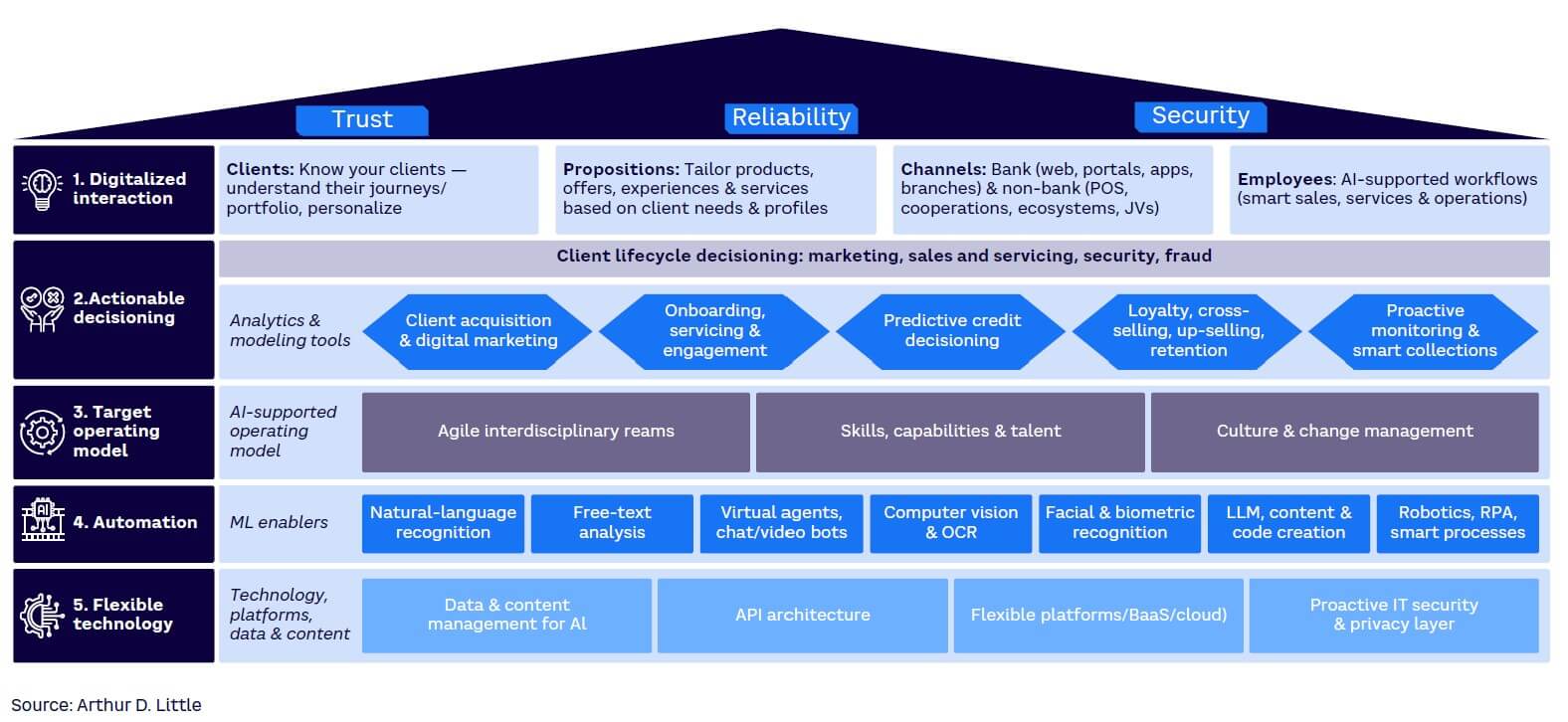
To achieve these goals, AI-enhanced banks use a sophisticated, multilayered approach designed to cater to every aspect of the banking experience. Imagine a typical retail-banking customer, Jane, is looking for a bank that offers a personalized and secure experience. As she begins her search, Jane discovers the AI-enhanced bank through targeted digital marketing (Layer 2a).
The bank’s online presence and omnichannel-built interface (Layer 1c) provide her with an engaging, easy-to-navigate experience. She’s immediately impressed by the level of personalization the bank offers, which is driven by its understanding of client needs and preferences (Layer 1a).
Jane decides to open an account with the AI-enhanced bank. During the onboarding process (Layer 2b), the bank’s virtual agents and chatbots (Layer 4c) help her understand the products and offers (Layer 1b) that best suit her financial needs. The AI-supported employee workflows (Layer 1d) ensure that the process is smooth and efficient. As Jane engages with the bank, the actionable decisioning tools (Layer 2) predict her creditworthiness, enabling the bank to make informed credit decisions (Layer 2c). The bank’s loyalty and retention programs (Layer 2d), which are fueled by AI-driven insights, keep Jane engaged and satisfied.
Throughout her banking journey, Jane’s transactions and data are proactively monitored (Layer 2e) by the bank’s fraud detection and IT security systems (Layer 5d) to ensure privacy and security. The bank’s flexible technology (Layer 5) allows for seamless integration with various platforms, data, and content management systems (Layers 5a, 5b, 5c), providing a smooth and efficient user experience.
As the bank optimizes and empowers its workforce, its target operating model (Layer 3) fosters an environment of interdisciplinary teams (Layer 3a), continuous skill development (Layer 3b), and a culture that embraces change management (Layer 3c).
In this way, the AI-enhanced bank’s approach addresses Jane’s expectations of trust, reliability, and security while delivering a personalized, seamless banking experience. Using the power of AI and advanced technologies, the bank can successfully adapt to the evolving needs of its customers, setting a new standard for retail banking.

Conclusion
DRIVING FINANCIAL SERVICES SALES THROUGH AI & DIGITALIZATION
Banks must transform to attract and retain customers, creating new revenue streams through digital channels. They need to shift their operating model to become AI-enhanced banks to deliver economic benefits. Achieving this in a complex, digital, and interconnected world requires:
- A well thought-out strategy, robust technology, marketing skills, and digital native resources.
- A redesigned digital customer acquisition and experience strategy that includes where and how to differentiate.
- Significant investment in developing and implementing new operational models utilizing AI, ML, and automation.
- An end-to-end process designed to:
- Humanize digital interactions.
- Reinvigorate brand purpose.
- Empower technology (especially AI).
- Reimagine branches to cater to client advice needs.
- Ensure continuous self-learning feedback loop through monitoring analysis and improvement.
Note
[1] Google recently announced that its cookie ban on the Chrome browser will be delayed until H2 2024. Other browsers, such as Mozilla Firefox, already have bans in place.

